Abstract
Case Report
Comparative Study of Enophthalmos Treatment with Titanium Mesh Combined with Absorbable Implant vs. Costochondral Graft for Large Orbital Defects in Floor Fractures
Malagón Hidalgo*, Héctor Omar, González Magaña, Fernando, Kalach Mussali, Alberto Jaime, Mejía Valero, Sergio Abraham, Vilchis López, Roberto, Araiza Gómez, Edgardo and Kalach Mussali
Published: 23 March, 2017 | Volume 2 - Issue 1 | Pages: 022-29
Introduction: Several treatment options are available for the optimal treatment for orbital fractures, depending on aesthetic and functional results after orbital wall reconstruction. The objective of this study is to compare the effect and safety of large orbital floor fractures with titanium mesh combined with poly-L-lactic acid/polyglycolic acid copolymer implants (Lactosorb®) vs. autologous costochondral graft. A wide range of permanent and biodegradable materials have been used successfully for orbital floor reconstruction, however they present with disadvantages for reconstruction of large defects, even if combined.
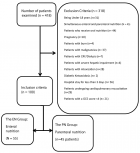
Patients and Methods: A retrospective cohort study of patients from Estado de México, México, with access to ISSEMYM health care service, presenting with orbital floor fracture treated at Department of Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery/Maxillofacial Surgery at ISSEMYM Medical Center Toluca between January 2007 and July 2010. Age, sex, etiology, clinical findings, fracture pattern, and treatment modality (Titanium mesh with absorbable implant vs. costochondral graft) were considered. Predictor and outcome variables as complications, inpatient, trauma- surgery interval, surgical time and donor site pain are considered.
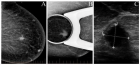
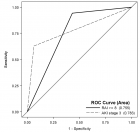
Results: Follow up of 21 patients (12 weeks) 17 male, 4 female, ages 22-63 was made. Enophthalmos, main objective of this study, was identified with statistical significance presenting 0% (n=0) post-op Group B patients and 30% (n=3) for Group A (p=0.049). Statistical significance was found referring to inpatient days between two groups being less for costochondral reconstruction patients (p=0.02). No pain in patients undergoing alloplastic surgery. An interesting result was that donor area analogue pain scale for costochondral graft was 2.9/10.
Conclusion: Surgical outcome and complications where evaluated comparing different materials for orbital floor reconstruction. Costochondral graft is a suitable choice when orbital reconstruction is indicated.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001007 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Orbital floor fracture; Orbital floor reconstruction; Autologous costochondral graft; Titanium mesh; Poly-L-lactic acid/polyglycolic acid copolymer implant
References
- Chang EW, Manolidis S. Orbital Floor Fracture Management. Facial Plast Surg. 2005; 21: 207-213. Ref.: https://goo.gl/SrnDOP
- Cole P, Kauffman Y, Hollier L. Principles of facial trauma: orbital fracture management. J Craniofac Surg. 2009; 20: 101-104. Ref.: https://goo.gl/7kgdP8
- Magaña FG, Arzac RM, De Hilario Aviles L. Combined Use of Titanium Mesh and Resorbable PLLA-PGA Implant in the Treatment of Large Orbital Floor Fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2011; 22: 1991-1995. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JcdNyQ
- Malagón Hidalgo H, González Magaña F, Rivera Estolano RT. Manejo del Enoftalmos como Secuela de Fracturas del Complejo Cigomático-Orbitario con Apoyo de Estereolitografía. Cir Plast Iberolatinoam. 2011; 37: 33-41.
- Jank S, Emshoff R, Schuchter B, Strobl H, Brandlmaier I, et al. Orbital Floor Reconstruction with Flexible Ethisorb Patches: A Retrospective Long-Term Follow-Up Study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003; 95: 16-22. Ref.: https://goo.gl/CuUKSQ
- Custer PL, Lind A, Trinkaus KM. Complications of supramid orbital implants. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 19: 62-67. Ref.: https://goo.gl/7Xagan
- Büchel P, Rahal A, Seto I, Izuka T. Reconstruction of Orbital Floor Fracture with Polyglactin 910/Polydioxanon Patch (Ethisorb): A Retrospective Study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63: 646-50. Ref.: https://goo.gl/2yvnwk
- Tuncer S, Yavuzer R, Kandal S, Demir YH, Ozmen S, et al. Reconstruction of Traumatic Orbital Floor Fractures with Resorbable Mesh Plate. J Craniofac Surg. 2007; 18: 598-605. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Q8yhlk
- Hollier LH, Rogers N, Berzin E, Stal S. Resorbable Mesh in the Treatment of Orbital Floor Fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2001; 12: 242-246. Ref.: https://goo.gl/sNVBuC
- Nam SB, Bae YC, Moon JS, Kang YS. Analysis of the Postoperative Outcome in 405 Cases of Orbital Fracture Using 2 Synthetic Orbital Implants. Ann Plast Surg. 2006; 56: 263-267. Ref.: https://goo.gl/zZSQWU
- Hwang K, You SH, Sohn IA. Analysis of Orbital Bone Fractures: A 12-Year Study of 391 Patients. J Craniofac Surg. 2009; 20: 1218-12123. Ref.: https://goo.gl/o0EnAj
- Mauriello JA Jr, Wasserman B, Kraut R. Use of Vicryl (Polyglactin-910) Mesh Implant for Repair of Orbital Floor Fracture Causing Diplopia: A Study of 28 Patients Over 5 Years. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 9: 191-195. Ref.: https://goo.gl/cSOJPu
- Uygur S, Cukurluoglu O, Ozmen S, Guclu TH, Sezgin B. Resorbable Mesh Plate in the Treatment of Blow-Out Fracture Might cause Gaze Restriction. J Craniofac Surg. 2009; 20: 71-72. Ref.: https://goo.gl/lBq0BZ
- Ellis E 3rd, Tan Y. Assessment of Internal Orbital Reconstructions for Pure Blowout Fractures: Cranial Bone Grafts versus Titanium Mesh. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61: 442-453. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Kr39Cn
- Kontio RK, Laine P, Salo A, Paukku P, Lindqvist C, et al. Reconstruction of Internal Orbital Wall Fracture with Iliac Crest Free Bone Graft: Clinical, Computed Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Follow-Up Study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 118: 1365-1374. Ref.: https://goo.gl/lzlKG0
- Park HS, Kim YK, Yoon CH. Various Applications of Titanium Mesh Screen Implant to Orbital Wall Fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2001; 12: 555-560. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Q9HBCW
- Xu JJ1, Teng L, Jin XL, Ji Y, Lu JJ, et al. Porous Polyethylene Implants in Orbital Blow-Out Fractures and Enophtalmos Reconstruction. J Craniofac Surg. 2009; 20: 918-920. Ref.: https://goo.gl/7QLqzI
- Lee HB, Nunery WR. Orbital Adherence Syndrome Secondary to Titanium Implant Material. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 25: 33-36. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qzuqgf
- Ng JD, Huyng TH, Burgett R. Complications of Bioabsorbable Orbital Implants and Fixation Plates. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 20: 85-86. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ghXcIL
- Malagón-Hidalgo HO, González-Magaña F, Ayala-Ugalde F, García-Cano E, Vilchis-López R. Experiencia a largo plazo con el uso de implantes absorbibles preformados para el tratamiento de fracturas orbitarias. Cir Plast. 2015; 25: 97-105. Ref.: https://goo.gl/GwMm2j
- Pietrzak WS, Kumar M. An Enhanced Strength Retention Poly (Glycolic Acid)-Poly (L-Lactic Acid) Copolymer for Internal Fixation: In vitro Characterization of Hydrolysis. J Craniofac Surg. 2009; 20: 1533-1537. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8AFss5
- Ahmad N, Lyles J, Panchal J, Deschamps-Braly J. Outcomes and Complications Based on Experience with Resorbable Plates in Pediatric Craniosynostosis Patients. J Craniofac Surg. 2008; 19: 855-860. Ref.: https://goo.gl/z0kgv3
- Kumar AV, Staffenberg DA, Petronio JA, Wood RJ. Bioabsorbable Plates and Screws in Pediatric Craniofacial Surgery: A Review of 22 Cases. J Craniofac Surg. 1997; 8: 97-99. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qUs8Mh
- Losken HW, van Aalst JA, Mooney MP, Godfrey VL, Burt T, et al. Biodegradation of Inion Fast-Absorbing Biodegradable Plates and Screws. J Craniofac Surg. 2008; 19: 748-756. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Yiyoqa
- Eppley BL. Bioabsorbable Plate and Screw Fixation in Orthognathic Surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2007; 18: 818-825. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JaFm97
- Park CH, Kim HS, Lee JH, Hong SM, Ko YG, et al. Resorbable Skeletal Fixation Systems for Treating Maxillofacial Bone Fractures. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 137: 125-129. Ref.: https://goo.gl/G7ZuJ6
- Nunery WR, Tao JP, Johl S. Nylon Foil “Wraparound” Repair of Combined Orbital Floor and Medial Wall Fractures. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 24: 271-275. Ref.: https://goo.gl/vpVOJ6
- Taban M, Nakra T, Mancini R, Douglas RS, Goldberg RA. Orbital Wall Fracture Repair Using Seprafilm. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 25: 211-214. Ref.: https://goo.gl/USNijd
- Garibaldi DC, Iliff NT, Grant MP, Merbs SL. Use of Porous Polyethylene with Embedded Titanium in Orbital Reconstruction: A Review of 106 Patients. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007; 23: 439-444. Ref.: https://goo.gl/o6BtgC
- Kontio R, Lindqvist C. Management of Orbital Fractures. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2009; 21: 209-220. Ref.: https://goo.gl/QaSBRj
- Clauser L, Galiè M, Pagliaro F, Tieghi R. Posttraumatic Enophtalmos: Etiology, Principles of Reconstruction, and Correction. J Craniofac Surg. 2008; 19: 351-359. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ulBiwO
Similar Articles
-
Comparative Study of Enophthalmos Treatment with Titanium Mesh Combined with Absorbable Implant vs. Costochondral Graft for Large Orbital Defects in Floor FracturesMalagón Hidalgo*,Héctor Omar,González Magaña,Fernando, Kalach Mussali,Alberto Jaime,Mejía Valero,Sergio Abraham,Vilchis López,Roberto,Araiza Gómez,Edgardo,Kalach Mussali. Comparative Study of Enophthalmos Treatment with Titanium Mesh Combined with Absorbable Implant vs. Costochondral Graft for Large Orbital Defects in Floor Fractures . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001007; 2: 022-29
Recently Viewed
-
The effect of frequency of sexual intercourse on coronary artery diseaseMehdi Karasu*,Özkan Karaca,Mehmet Ali Kobat,Tarık Kıvrak,Mehmet İkbal İpek. The effect of frequency of sexual intercourse on coronary artery disease. Arch Vas Med. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.avm.1001015; 6: 001-004
-
A Case Report on Paradoxical EmboliYou Li* and Jason Wheeler. A Case Report on Paradoxical Emboli. Arch Vas Med. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.avm.1001019; 8: 004-007
-
Precision and personalized vaccines needed to face COVID-19 pandemicDahmani Fathallah M*. Precision and personalized vaccines needed to face COVID-19 pandemic. Insights Clin Cell Immunol. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001017; 5: 003-003
-
NAD⁺ Biology in Ageing and Chronic Disease: Mechanisms and Evidence across Skin, Fertility, Osteoarthritis, Hearing and Vision Loss, Gut Health, Cardiovascular–Hepatic Metabolism, Neurological Disorders, and MuscleRizwan Uppal,Umar Saeed*,Muhammad Rehan Uppal. NAD⁺ Biology in Ageing and Chronic Disease: Mechanisms and Evidence across Skin, Fertility, Osteoarthritis, Hearing and Vision Loss, Gut Health, Cardiovascular–Hepatic Metabolism, Neurological Disorders, and Muscle. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001032; 10: 001-009
-
Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and RehabilitationCristina Popescu, Mircea-Sebastian Șerbănescu, Gigi Calin*, Magdalena Rodica Trăistaru. Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and Rehabilitation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001030; 8: 004-012
Most Viewed
-
Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization)Dasse Sery Romuald*, KL Siransy, N Koffi, RO Yeboah, EK Nguessan, HA Adou, VP Goran-Kouacou, AU Assi, JY Seri, S Moussa, D Oura, CL Memel, H Koya, E Atoukoula. Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization). Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001035; 8: 007-012
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037
-
Snow white: an allergic girl?Oreste Vittore Brenna*. Snow white: an allergic girl?. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001029; 6: 001-002
-
Cytokine intoxication as a model of cell apoptosis and predict of schizophrenia - like affective disordersElena Viktorovna Drozdova*. Cytokine intoxication as a model of cell apoptosis and predict of schizophrenia - like affective disorders. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001028; 5: 038-040

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."